背景介绍
循环肿瘤细胞(circulating tumor cell, CTC)是指由原发灶脱落,侵入血液循环的肿瘤细胞。CTC能逃避机体免疫,在原发或远处脏器驻留,从而形成复发、转移病灶。原发肿瘤生长到一定阶段,会侵袭周围血管,肿瘤细胞会首先通过整联蛋白附着在血管基底膜处生长;当肿瘤细胞数量逐渐增多,其分泌的基质金属蛋白酶也逐渐增加,通过逐步消化掉IV型胶原蛋白,突破基底膜屏障,进入血液,即被称为CTC;CTC进入血液后,会随着血液循环游走全身,形成复发转移,不同肿瘤的远处转移与血流分布有很大关系。例如乳腺癌一般会在肺部有继发性病灶,而结肠癌则常形成肝转移。
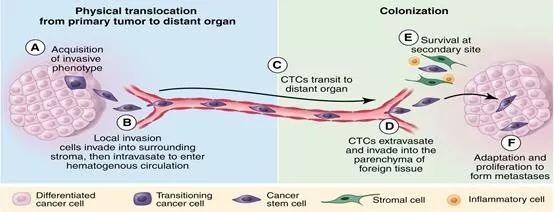
循环肿瘤细胞是近30年来研究应用的仅有的几个新型肿瘤分子标志物之一。通过检测CTC数量和蛋白表达可对肿瘤进行确诊、判断预后、监控疗效。例如,当CTC出现上皮间质转换(EMT)、过表达上皮细胞粘附分子往往提示肿瘤患者预后不佳;通过对比手术或放化疗前后血液中CTC数量,可以判断治疗是否有效,具有重要的临床研究及应用价值。
参考文献:
[1] Inhestern J, Oertel K, Stemmann V, et al. Prognostic Role of CirculatingTumor Cells during Induction Chemotherapy Followed by Curative Surgery Combinedwith Postoperative Radiotherapy in Patients with Locally Advanced Oral andOropharyngeal Squamous Cell Cancer[J]. Plos One, 2015, 10(7).
[2] Li T T, Liu H, Li F P, et al. Evaluation ofepithelial-mesenchymal transitioned circulating tumor cells in patients withresectable gastric cancer: Relevance to therapy response[J]. World Journal of Gastroenterology, 2015, 21(47):13259.
[3] Nieva J, Wendel M, Luttgen M S, et al.High-definition imaging of circulating tumor cells and associated cellularevents in non-small cell lung cancer patients: a longitudinal analysis.[J].Physical Biology, 2012, 9(1).
[4] Liu Y, Ling Y, Qi Q, et al. Prognostic valueof circulating tumor cells in advanced gastric cancer patients receivingchemotherapy.[J]. Molecular & Clinical Oncology, 2017, 6(2):235.
